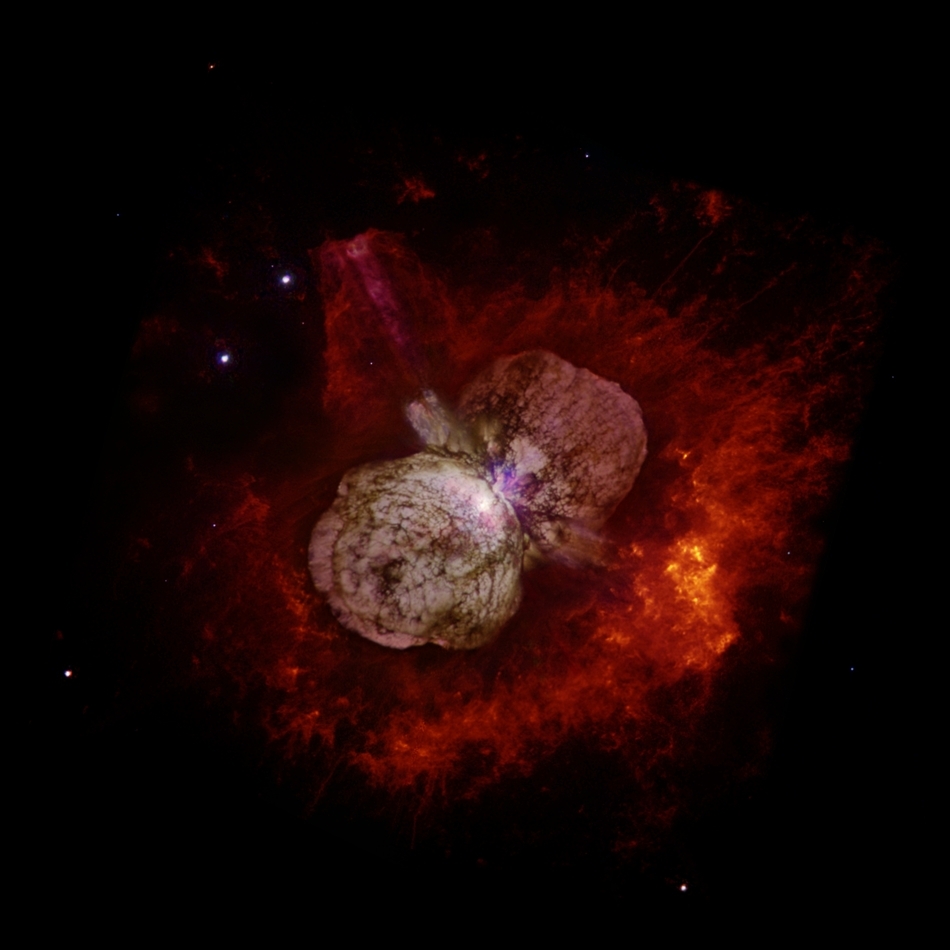
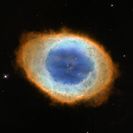
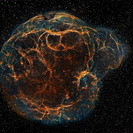
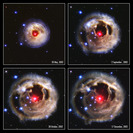
This is what it looks like when a star is fighting against running out of fuel in the last phase of its life. Eta Carinae is not a normal star; with its 120 solar masses it is one of the most massive known stars as of today. It fuses heavier and heavier elements to nurse its need for energy in order to prevent itself from collapsing. With the enormous amount of heat produced in the core, Eta Carinae blasts away its outer layers of gas and dust into the surrounding area. Eta Carinae will end its life in a violent event called a supernova. If you are interested in how such events take place don't miss our supernova article.
Fortunately the supernova is only expected within the next million years and Eta Carinae is at a relatively safe distance of about 8000 light years from us. A supernova would most probably not affect terrestrial life forms directly; it would just damage the upper atmosphere and satellites. More details of the possible effects on Earth can be found in the wikipedia article.
A violent outburst visible around the year 1843 created the two large lobes and the equatorial disk with matter receding from the star at speeds of about 1 million km/h.
If interested, read more about: Supernova