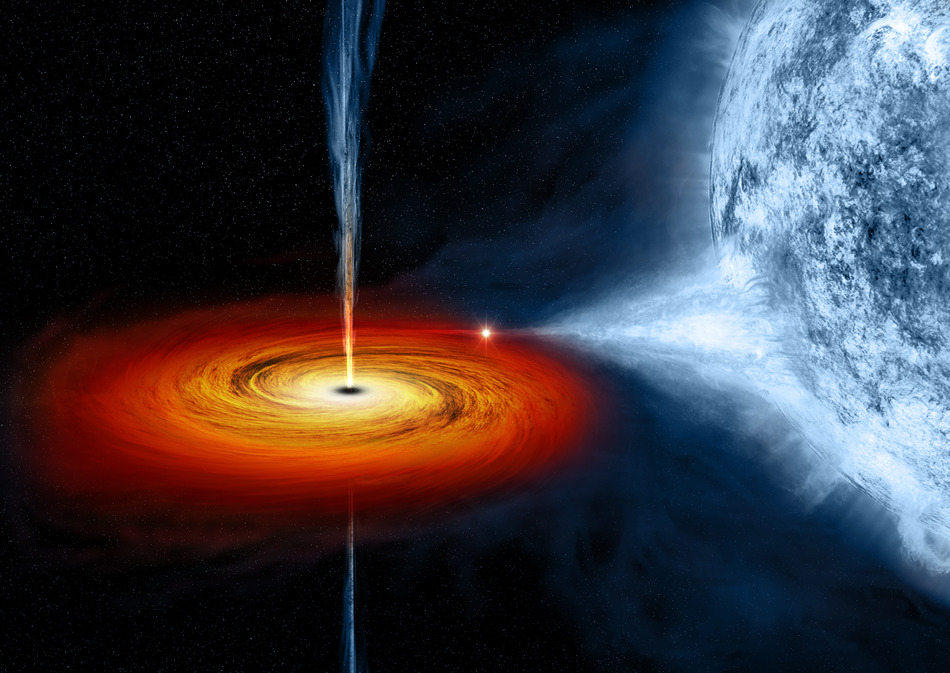
Cygnus X-1 (the image is an artist's impression) is a typical stellar mass black hole. At a distance of 6000 light years from Earth and an estimated mass of 14.8 solar masses it is one of the closer black holes to Earth. It's the result of a core collapse at the end of the life of a star of 30 to 40 solar masses. More details can be found in our article about supernova.
In this image the black hole attracts matter from a nearby star and builds an accretion disk. It's not so uncommon for stars to orbit each other so closely: more than half of all stars live in binary (or even multiple) star systems with two or more stars orbiting around each other. The released potential energy and friction within the accretion disk heats up the matter to enormous temperatures of tens of millions or even to more than a hundred million kelvin.
Only very few stars are heavy enough to form a black hole at the end of their lives, but if this is the case the chances are quite good that sooner or later they start attracting matter from the accompanying star, such as in the case of Cygnus X-1.
If interested, read more about: Supernova - Black hole